After Test Summary
Passed! The real exam was much easier than the practice test for me. Studying the Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, and Analytics in more-depth helped a lot! A few things on the test that I wasn’t strong on were:
- Lightning For Outlook
- Time-based Workflow Actions. One question asked what happens to a pending time-based workflow action if it no longer meets the criteria. I answered that it still runs but wasn’t sure.
- Lead Conversion process & mapping. Thankfully, I knew that a lead can convert into an Account, Contact & Opportunity.
Recommended Path for Others
- Use Salesforce for 6 months or so.
- Complete the Admin Prep Trailmix. This will likely take you 20-30 hours, especially if you do the security super badge and reports & dashboards super badge. Despite my comments regarding this below, this was helpful for the real exam.
- Take the Admin Practice Test on Web Assessor for $20. Since it’s unproctored, you can do it right from your own computer whenever you want like a maintenance exam. The results will inform you where you need to study more. This is the only “official” practice test and I wish there were others.
- When reading help guides and other Salesforce documentation, pay special attention to the “Notes, Considerations, & Limits” sections. These usually come up in an exam question or two in every certification and help eliminate choices from other questions. For example, one question I had today was “What’s the limit on how many filters can be in a dashboard?”. In the practice test, there was a similar dashboard limit question: “How many components can be on a dashboard?”. I’ll let you find the answers 😉 For reports & dashboards, I highly recommend reading the Analytics PDF starting with page 780 or so and reading the rest. All my analytics info below is from that.
- Use my General Certification Tips for other prepping tips. Good luck!
Overview
This is the study guide prepared for myself for the Salesforce Admin Certification Exam. This is my first in the Throwing Down the Certification Gauntlet #2. I’m actually quite intimidated by this one despite having 7 years of experience and 10 other certifications currently because I don’t do admin tasks in my day-to-day work. I also failed the Salesforce Practice Test in Web Assessor by 2 answers with a 61% score.
The Exam Guide details what to expect, the content tested, and how many questions come from each content area. To prepare, I researched various help, videos, and blogs covering each topic area and practiced using them in a dev org. I also took the Salesforce Practice Test in Web Assessor which cost only $20 and is unproctored so you take it when you’re ready, similar to a maintenance exam. The practice exam results detail your score in each topic area. Analytics and Dashboards, Sales & Service were my weakest areas so most of my prep time was spent there. I didn’t bother reviewing areas that are 1% because that means there’ll be 1 question in the exam.
Resources
Here are resources that I came across but didn’t use all of them. The trailmix was ok but very high-level. It didn’t go into any level of depth that is needed. I took the Practice Test after completing it and found it rather inadequate so I turned to other resources for additional information.
- We Are 4C: Tips For Passing Administrator Exam
- Trailmix
- Certification Guide
- Focus On Force: Administrator Study Guide – $19 – Haven’t used it but have heard good things
- Mike Wheeler’s Udemy Courses – Various Prices – Haven’t used them but have heard good things
- User Guides Reference
- Set Up & Maintain Your Salesforce Organization
- Sales Basics
- Sales Productivity
- Service Cloud
- Admin Tip Sheets & User Guides Reference List
- Standard Object List
- Analytics PDF – Most comprehensive guide I’ve come across for Reports & Dashboards! A bit lengthy but seems to contain all the info.
Exam Outline
- Organization Setup – 2%
- Describe the information found in the company information (e.g., fiscal
year, business hours, currency management, default settings). - Distinguish between the various UI features that an administrator
controls, including the implications (e.g., UI settings, search settings, list
views, home page layouts).
- Describe the information found in the company information (e.g., fiscal
- User Setup – 7%
- Identify the steps to set up and/or maintain a user (e.g., assign licenses,
reset passwords, and resolve locked user accounts). - Understand the implications of activating, deactivating, or freezing a
user.
- Identify the steps to set up and/or maintain a user (e.g., assign licenses,
- Security & Access – 14%
- Explain the various organization security controls (e.g., passwords, IP
restrictions, identity confirmation, network settings). - Given a user request scenario, apply the appropriate security controls
based on the features and capabilities of the Salesforce sharing model
(e.g., organization-wide defaults, roles and the role hierarchy, manual
sharing, sharing rules and public groups). - Given a scenario, determine the appropriate use of a custom profile or
permission set using the various profile settings and permissions. - Describe how folders can be used to organize and secure
communication templates, dashboards, and reports.
- Explain the various organization security controls (e.g., passwords, IP
- Standard & Custom Objects – 15%
- Describe the standard object architecture and relationship model.
- Explain how to create, delete, and customize fields and page layouts on
standard and custom objects, and understand the implications of
deleting fields. - Given a scenario, determine how to create and assign page layouts,
record types and business processes for custom and standard objects
- Sales & Marketing Applications – 15%
- Given a scenario, identify the capabilities and implications of the sales
process. - Given a scenario, identify the appropriate sales productivity features
using opportunity tools and know when products and Price Books should
be used. - Describe the capabilities of lead automation tools and campaign
management. - Describe the capability of Salesforce Content.
- Given a scenario, identify the capabilities and implications of the sales
- Service & Support Applications – 12%
- Describe the capabilities of case management (e.g., case processes, case
settings, and case comments). - Given a scenario, identify how to automate case management (e.g., case
assignment, auto-response, escalation, web-to-case, email-to-case, case
teams). - Describe the capabilities of solution management and Salesforce
Knowledge. - Describe the capabilities of the Community application (e.g. Ideas,
Answers).
- Describe the capabilities of case management (e.g., case processes, case
- Activity Management & Collaboration – 3%
- Describe the capabilities of activity management (e.g., manage tasks,
events, public calendars, multi-day events. - Describe the features of Chatter (e.g., feed, groups, following, security).
- Describe the capabilities of activity management (e.g., manage tasks,
- Data Management – 8%
- Describe the considerations when importing, updating, transferring, and
mass deleting data (e.g., CSV files, data quality, field mapping, record
IDs, external IDs, duplicate records). - Given a scenario, identify tools and use cases for managing data (e.g.,
dataloader, data import wizard). - Describe the capabilities and implications of data validation tools.
- Describe the different ways to back up data (e.g., data export service,
exports, dataloader).
- Describe the considerations when importing, updating, transferring, and
- Analytics – Reports & Dashboards – 10%
- Describe the options available when creating or customizing a report
(e.g., report type, report format, fields, summarizing data, filtering data,
charting, scheduling, and conditional highlighting). - Describe the impact of the sharing model on reports
- Describe the options available when creating and modifying dashboards
(e.g., dashboard components, data sources, chart types, scheduling, and
running user). - Describe the capabilities of custom report types
- Describe the options available when creating or customizing a report
- Workflow / Process Automation – 12%
- Given a scenario, identify the appropriate automation solution based on
the capabilities of workflow/process. - Describe capabilities and use cases for the approval process
- Given a scenario, identify the appropriate automation solution based on
- Desktop & Mobile Administration – 1%
- Describe the capabilities of the Salesforce Mobile App.
- Describe the installation and synchronization options of Salesforce
Lightning for Outlook.
- AppExchange – 1%
- Identify use cases for AppExchange applications
Standard Object Architecture
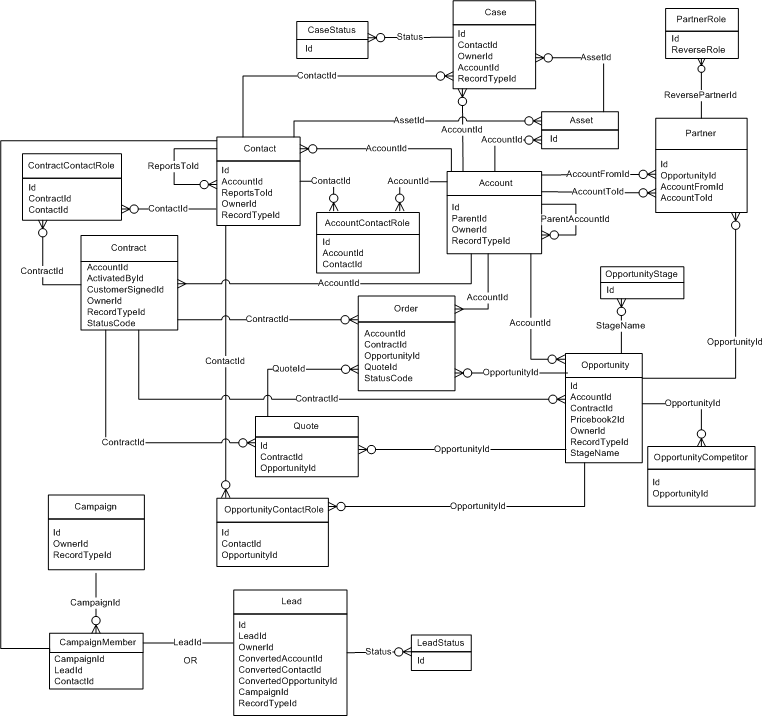
Sales Cloud
- Accounts – Represents an individual account, which is an organization or person involved with your business (such as customers, competitors, and partners).
- Contacts – Represents a contact, which is a person associated with an account.
- Opportunity – Represents an opportunity, which is a sale or pending deal.
- Opportunity Line Item – Represents an opportunity line item, which is a member of the list of Product2 products associated with an Opportunity.
- Product – Represents a product that your org sells.
- Leads – Represents a prospect or lead.
- Campaigns – Represents and tracks a marketing campaign, such as a direct mail promotion, webinar, or trade show.
- Campaign Members – Represents the association between a campaign and either a lead or a contact.
- Quote – The Quote object represents a quote, which is a record showing proposed prices for products and services. Available in API version 18.0 and later.
- Quote Line Item – The QuoteLineItem object represents a quote line item, which is a member of the list of Product2 products associated with a Quote, along with other information about those line items on that quote. Available in API version 18.0 and later.
- Contract – Represents a contract (a business agreement) associated with an Account.
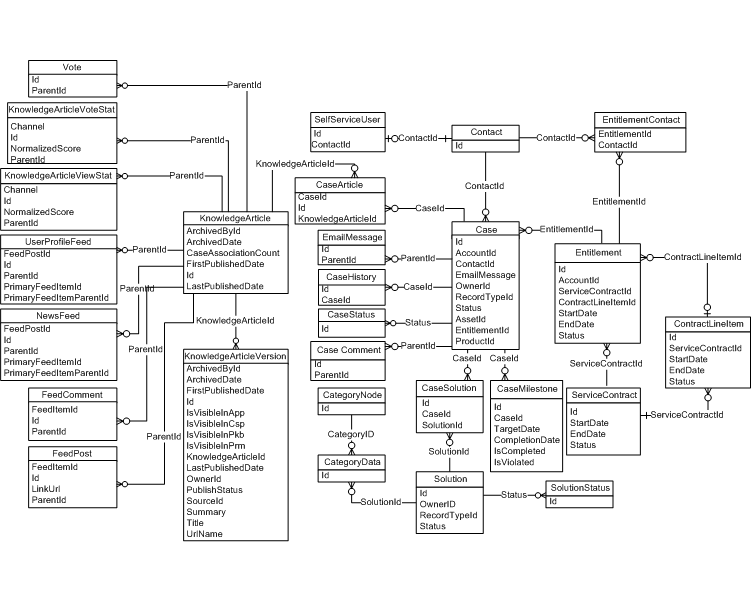
Service Cloud
- Case – Represents a case, which is a customer issue or problem.
- Case Milestone – Represents a milestone (required step in a customer support process) on a Case. This object is available in API version 18.0 and later.
- Entitlement – Represents the customer support an account or contact is eligible to receive. This object is available in API version 18.0 and later. Entitlements may be based on an asset, product, or service contract.
- Solution – Represents a detailed description of a customer issue and the resolution of that issue.
- Knowledge Article – Provides read-only access to an article and the ability to delete the master article. This object is available in API version 19.0 and later.
- KnowledgeArticleViewStat – Provides statistics on the number of views for the specified article across all article types. This object is read-only and available in API version 20 and later.
Sales Cloud
Sales Process
A sales process is used to determine which opportunity stages are selectable when record types are enabled. A Sales process is not required if record types are not enabled. Source
Price Books & Assigning
When is a single price book appropriate?
At least one price book must be configured and active in order to add products to either an opportunity or a quote.
Lead Assignment Rules
Specify how leads are assigned to users or queues as they are created manually, captured from the web, or imported via the Data Import Wizard. Source
These assignment rules specify a criteria and if met, assign ownership to the specified User or Queue.
Lead Processes
A lead process allows you to define or customize status values or stages for leads. Source
After one creates a Lead Process, where one specifies the status values, it has to be assigned to one or more record types to be used. Essentially the same process as Sales Processes but with just statuses. Lead Statuses are just picklist values and don’t have other special attributes like Opportunity Stages.
Web-to-Lead
This capability lets you generate a form within Salesforce using specified fields. Salesforce generates the raw html that can be embedded in a website. When the form is submitted, it sends the information to Salesforce and creates a Lead. Source
Lead Auto-Response Rules
Send automatic email responses to lead or case submissions based on the record’s attributes. Set up auto-response rules to send quick replies to customers to let them know someone at your company received their inquiry or details about their issue.
Sales and service reps can find the email responses in the Activity History related list of the lead or contact and in the Email related list on cases.
Campaign Management
Campaign Management Implementation Guide
5 Tips To Use Salesforce Campaigns Effectively
CRM Content
Organize, share, search, and manage content within your organization and across key areas with CRM Content. Content includes al file types, from traditional business documents to audio files, video files, Web pages, and Google docs. Files are stored in Libraries. Libraries can be public or private.
Case Management
Case Management Implementation Guide
Case Contact Role
Allows more than one contact to be associated to a case. They’re displayed in the case’s Contact Roles related list.
Case Hierarchies
Allows one case to be associated to another via the Parent Case lookup field. You can view the hierarchy with the “View Hierarchy” button.
Suggested Solutions
Enabling the Suggested Solutions button on case detail pages allow support reps to view solutions that may help them solve the particular case they are solving. Have to enable Suggested Solutions in Support Settings.
Case Comment Notification
Enable the Send Email Notification option on case edit pages so that support reps can send an email to any contact when they have added a comment to a case. The “Enable Case Comment Notification to Contacts” checkbox has to be checked in Support Settings in Setup first.
- case processes, case
settings, and case comments
Case Page Layouts
There are two types:
- Detail Page
- Close Case Page
Case Assignment Rules
Assignment Rules automatically assign new cases to the appropriate user or queue. You can make users members of a queue and any member can take ownership of the cases within the queue. They function just like Lead Assignment rules where if a new case matches the criteria in a rule entry, the case is assigned to the specified user or queue.
One can also use an assignment rule to add predefined case teams to a case.
Default Case Owner
The user or queue assigned ownership of the queue when no assignment rules apply. This is configured in Support Settings.
Auto-Response Rules
Allows an admin to specify criteria for a case and if met, automatically email the submitted via an email template
Escalation Rules
Your organization may have a process for escalating cases that remain open beyond a specified period of time. Create an escalation rule that specifies what actions to take when cases are not resolved with a designated length of time.
Support Processes
Create and maintain multiple support processes for your organization to use. Support processs use the status field to identify a case within the support lifecycle. After creating a new support process, associate it with one or more Case Record Type to apply it to new cases.
Analytics – Reports & Dashboards
- Describe the options available when creating or customizing a report
(e.g., report type, report format, fields, summarizing data, filtering data,
charting, scheduling, and conditional highlighting). - Describe the impact of the sharing model on reports
- Describe the options available when creating and modifying dashboards
(e.g., dashboard components, data sources, chart types, scheduling, and
running user). - Describe the capabilities of custom report types
Analytics PDF – 1100ish pages but the most comprehensive guide I’ve discovered. Skip to Reports and Dashboards for that info.
Reports Formats
- Tabular – Similar to a spreadsheet with rows and columns. Best for lists with a single grand total. Can’t be used to create groups or charts and can’t be used in dashboards unless rows are limited.
- Summary – Similar to tabular but also allow users to group rows of data, view subtotals, and create charts. They can be used as the source report for dashboard component. Can have up to 3 groupings.
- Matrix – A report grouped by row and column. Can be source for dashboard components. Use this for comparing related totals, especially if you have large amounts of info to summarize and you need to compare values in different fields. Can have up to 2 row groupings and 2 column groupings.
- Joined – Lets your create report blocks that provide different views. Each block acts like a sub-report with its own fields, columns, sorting and filtering. Can have up to 3 groupings.
Summary Field
A summary field contains numeric numeric values for which you want to know the sum, average, min or max. Summaries can’t be placed after custom summary formulas or record count.
Report Charts
Charts provide a visual way to understand the data in your report. Charts appear at the top of the report. Your report must have at least one grouping before you can add a chart. They can be added to any summary or matrix report.
Bucket Fields
Buckets are a custom way to group values on a field without a custom summary formula or custom field. They can be used on numeric, picklist and text fields.
Limits & Considerations
- Each report can have up to 5 bucket fields.
- Each bucket field can contain up to 20 buckets.
- Each bucket can contain up to 20 values.
- A bucket is report specific. Have to recreate it for other reports.
- Aren’t available in reports with external objects.
Summary Formulas
Use summary formulas to logically evaluate and do math with report results. They require at least one group.
Summary Formula Limitations
- Can’t reference other summary formulas
- Can’t group by summary formulas.
- Aren’t filterable
- Must contain 3900 or fewer characters.
Dashboards Chart Types
Bar Charts
Shows values as horizontal lengths. Use when you have a summary report with a single column grouping, or you only want to display one grouping.
Stacked Bar Charts
Display when you have multiple groupings and are interested in proportions between values in each grouping and each grouping’s total. For example, compare the status of leads by campaign, and also to compare the totals for each status.
Line Charts
Good for showing changes in the value of an item over time.
Donut Charts
Good for multiple groupings and want to show the proportion of a single value for each grouping against the total and the total amount itself.
Funnel Charts
Use when you have multiple groupings in an ordered set and want to show proportions among them.
Scatter Charts
Use to show meaningful information using one or two groups of report data plus measures.
Gauge Charts
Used to see how far you are from reaching a goal.
Metric Charts
Use when you have one key value to display.

A very nice article that covers the entire Salesforce Admin Certification exam preparation.